BlackBooks
Cheatsheets to double check one’s work
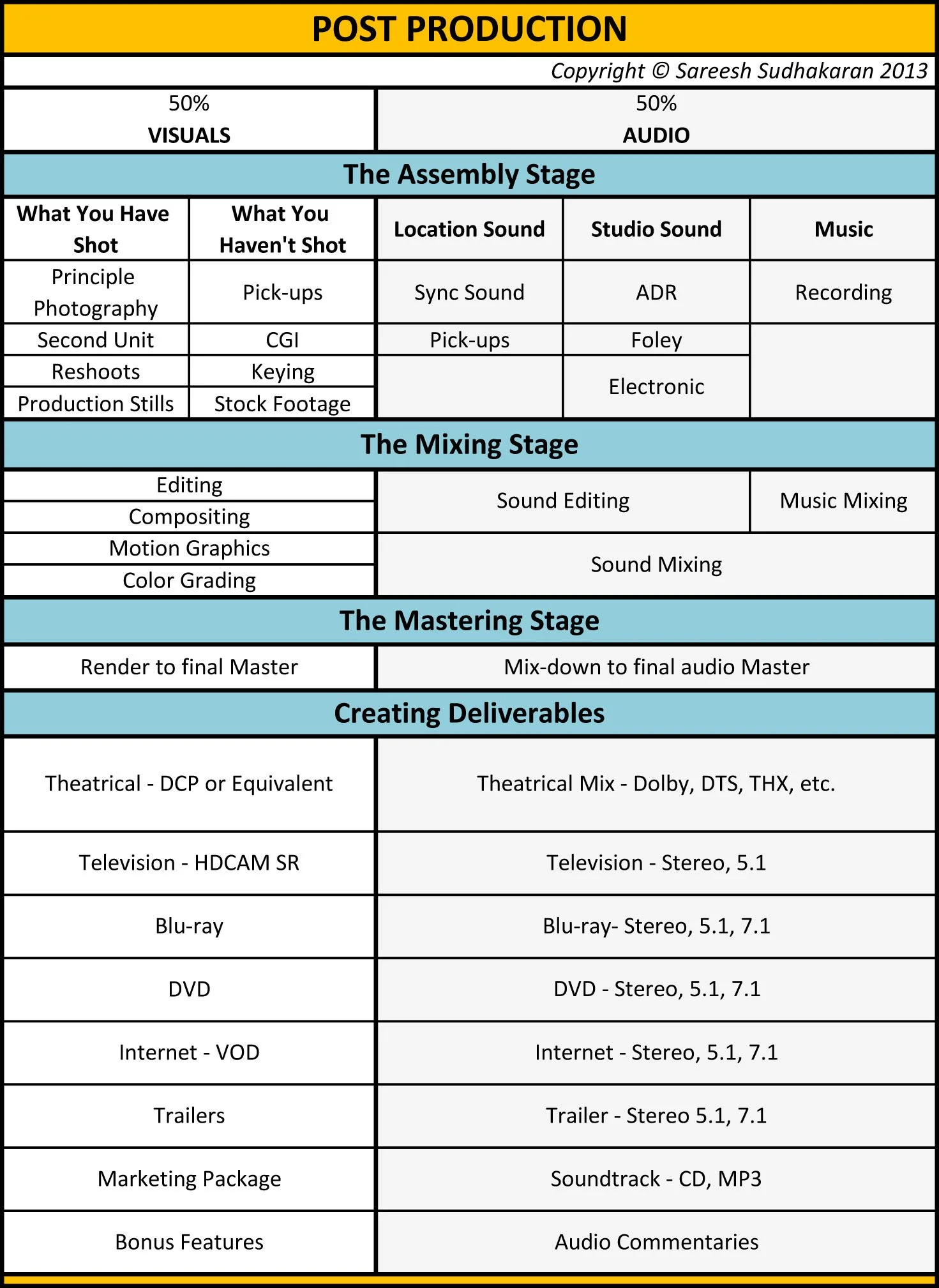
Delivery Standards
Streaming Services
Netflix | Disney+ | AppleTV | Amazon Prime | Hulu | HBOMax | ShowMax | Youtube
Netflix : https://partnerhelp.netflixstudios.com/hc/en-us/categories/1500000000761-Delivery
Disney+ : https://mediatechspecs.disney.com/#/
Apple TV : https://help.apple.com/itc/TV/channels/subvideospec/#/apdA45d16ccc
Amazon Prime : https://videocentral.amazon.com/home/help?topicId=GDDDXTDKXPSEY7JF&ref_=avd_sup_GDDDXTDKXPSEY7JF
Hulu : https://assets.hulu.com/portaldocuments/ContentPartnerGuidebook_v5.0.pdf
HBOMax : https://partnerhub.warnermediagroup.com/specifications-and-guides/licensed/licensed-content-sdr
ShowMax : MIA
Youtube : https://support.google.com/youtube/answer/4603579?hl=en
Broadcasters
DSTV : https://www.dstv.com/m-net/en-za/page/commissioning-protocol
SABC : https://www.sabc.co.za/sabc/sabc-technical-standards-for-delivery-of-hd-tv-programmes/
Camera Manufacturers
Camera Sensors:
ARRI:
Alexa Classic: ALEV3
Amira: ALEV3
Alexa Mini LF: ALEV A2X
Alexa 35: ALEV4
Alexa 65: ALEV3 A3X
Sony: https://www.sony-semicon.com/en/products/is/camera/index.html
Blackmagic Design:
BMPCC4K: Sony IMX294CJK https://www.sony-semicon.com/files/62/flyer_security/IMX294CJK_Flyer.pdf
RED:
Nikon: https://www.digitalcameraworld.com/news/these-32-nikon-cameras-are-sonys-in-disguise
Panasonic: https://www.bmcuser.com/forum/blackmagic-camera/general-discussion/22270-sony-imx294-same-sensor-in-blackmagic-pocket-4k-and-gh5s
Camera Manufacturer > Camera Model > Codecs & settings > Charts > Notes
-
Alexa Classic: ALEV3
Amira: ALEV3
Alexa Mini LF: ALEV3 A2X
Alexa 65: ALEV3 A3X
Alexa 35: ALEV4
-
Venice
FX9
FX6
FX3
FX30
https://www.alldatasheet.com/datasheet-pdf/pdf/1266625/SONY/IMX294CJK.html
-
BMPCC OG
BMPCC4k: Sony IMX294CJK
BMPCC6K
Ursa
Ursa 12k
-
GH5: Sony IMX294
-
-
Hardware Specifications
Given a minimum delivery standard of intra, 10-bit, 4K, with time-code:
the cameras below are 'delivery compatible’
Pipeline:
Delivery Standards
Hardware Compatibility
Software Compatibility
Hardware Specifications
Codecs and Containers
Data Rates & Optimisations
Tools
Mac & Windows HDD compatibility (TLDR; just use exFAT)
SD Card & Codec Compatibility
Ethernet
https://www.electronics-notes.com/articles/connectivity/ethernet-ieee-802-3/cables-types-pinout-cat-5-5e-6.php
Hardware Compatibility
Display Standards:
Display Protocols:
HDMI
DP
(Temporal) Compression: Interframe
Interframe, or temporal, compression reduces file sizes by eliminating redundant information between multiple frames of video. This is achieved by identifying and encoding only the changes between successive frames and eliminating areas that remain identical between them.
For example, the background of an image may remain unchanged while the subject of the video moves throughout the video. Instead of retaining the unchanging background in every frame, it can be retained in the first frame and used for all subsequent frames.
The process begins with selecting a keyframe (also called an I-frame) which is a fully intact frame and will serve as the reference for subsequent frames. Following the keyframe are P-frames and B-frames which will not be retained in full. Instead, only the changes relative to the keyframe are saved. P-frames (Predictive frames) store changes based on the preceding frames. B-frames (Bi-directional frames) retain information from both previous and subsequent frames in order to determine the minimal changes needed to represent the original video. This drastically reduces the amount of information saved in each video frame and subsequently significantly reduces file size. While it is efficient in file size reduction, it can affect image quality and introduce artifacts in situations with fast-moving and unpredictable elements.
Used for: Viewing
-
Adobe Premiere Pro is a videly used video editor, however, it has a considerable flaw when it comes to using the applicatino for ‘industry standard’ work.
Premiere Pro defults to 8-bit. Worse, effects that don’t feature GPU acceleration will crush the clips they are applied on down -to 8-bits.
-
A bit-depth of 8 limits each colour channel to 256 possible values. While this limitation is fine for delivery, it produces compression artifacts in various post-production workflows and is actively desctutive to any to footage recorded at a higher bit-depth.
-
Description text goes here
Adobe Premiere Pro is a videly used video editor, however, it has a considerable flaw when it comes to using the applicatino for ‘industry standard’ work.
Premiere Pro defults to 8-bit. Worse, effects that don’t feature GPU acceleration will crush the clips they are applied on down -to 8-bits.
Why does this matter?
A bit-depth of 8 limits each colour channel to 256 possible values. While this limitation is fine for delivery, it produces compression artifacts in various post-production workflows and is actively desctutive to any to footage recorded at a higher bit-depth.
Unless Premier Pro is setup correctly, all imported and exported footage will be reduced to 8-bit. Even when setup correctly, certain FX with Premier Pro descructively reduce the bit-depth of correctly imported video files.
For this reason I prefer not to use Premiere Pro.
Premier Pro has a problem
*
Premier Pro has a problem *
The Solution:
As stated, there is no way to force all aspects of Premiere Pro to perform in a >8-bit space, however, the Frame.io article below outlines the best practices for setting up Premiere Pro and Premiere Pro projects.
https://blog.frame.io/2021/06/07/premiere-pro-max-render-quality-max-bit-depth/
DaVinci Resolve: All Things To All Editors
Blackmagic’s DaVinci Resolve has been, for some time, the most accessible media application capable of industry standard workflows.
vs
Intraframe: (Spatial) Compression
This technique compresses each frame individually by eliminating redundant information within a single frame. This is achieved by analyzing segments of the image and identifying regions with minimal variation and representing them more efficiently.
For example, the clear blue sky in the image below has very little variation between pixels, so those regions can be represented by a larger block of uniform color and texture. This reduces the amount of information that needs to be retained and will not drastically affect the final image quality.
In contrast, the areas with more complexity and color variation cannot be compressed to the same degree and more information needs to be retained in these regions. Spatial compression thus reduces file size while maintaining a high-quality image by retaining information in complex and highly detailed regions while reducing information in simple and less important areas.
Used for: Working
Container Support:
DCP
MXF
XAVC
MOV/ProRes
DNxHR
Premier to Davinci round-trip
What are EDL, XML, and AAF files?
EDL, XML, and AAF files reference the information and structure in your editing timeline such as your source media, in and out points, edits/cuts, duration, transitions, markers, etc. These files are used to rebuild your exact cut in another software.
Because EDL, XML, and AAF files are used throughout the post-production cycle — not only for color — it’s important to understand how to export them in general, not just if you’re going to be using Premiere Pro and DaVinci Resolve. VFX artists use the same files, for example.
EDL (Edit Decision List)
This is the simplest of the three files. EDLs are plain text files that contain basic information about your edit from a single track of your timeline. It supports one video track and four audio tracks per EDL. This one is best used as a backup reference.
XML (Extensible Markup Language)
XMLs are also plain text files like EDLs but contain way more information, including things like sizings, transitions, time remapping, and other important metadata. XMLs support multiple video tracks, unlike EDL files.
AAF (Advanced Authoring Format)
Last, but definitely not least, AAFs. This one is a multimedia file format and can include video, audio, and other important metadata needed to recreate the exact cut in another software. AAF is the one that includes the most data out of the three and therefore the heaviest.
Codec Support
Software Compatibility
Codecs
-
Motion JPEG
JPEG 2000 (ISO/IEC standard)
Apple ProRes 422/4444
AVC-Intra
AVC-Ultra
XAVC-1
CineForm HD
-
Apple ProRes RAW
ArriRaw
BlackMagic RAW
Canon CRX
CinemaDNG
Cintel RAW
Redcode RAW (modified JPEG 2000)
-
RGB 4:4:4 (only linear, transfer-converted and bit-reduced also sort of compression up to about 3:1 for HDR)
YUV 4:4:4/4:2:2/4:1:1/4:2:0 (all lower 4:4:4 is spatially compressed up to 2:1 for 4:2:0 with specific colour distortions).
10-bit uncompressed video
Composite digital signal - used by SMPTE D-2 and D-3 broadcast digital videocassettes
Avid DNxUncompressed
V210
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Uncompressed_video#:~:text=Data%20rates,-Uncompressed%20video%20has&text=data%20rate%20%3D%20color%20depth%20%C3%97,%C3%97%2024%20%3D%2058.9%20Mbit%2Fs
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Color_depth
-
H.264
H.265
Motion JPEG 2000
JPEG XS
AV1
VP9
-
MPEG-4
H.264
HEVC
AVI
Apple Video - QuickTime
VP9
MXF:
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Material_Exchange_Format
Codec Comparison
by
| Codec | Frame size | Mb/s (24p) | GB/hr (24p) | Bitrate type | Lossyness | Chroma | Bit depth | Create on Mac/PC |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cineform 10-bit HD Film Scan | 1920 x 1080 | 100 | 45 | Variable | 3 Minor | 4:2:2 | 10-bit | Yes |
| Cineform 10-bit HD Film Scan 2 | 1920 x 1080 | 180 | 81 | Variable | 2 Minimal | 4:2:2 | 10-bit | Yes |
| Cineform 10-bit HD High | 1920 x 1080 | 85 | 38 | Variable | 4 Some | 4:2:2 | 10-bit | Yes |
| Cineform 10-bit HD Low | 1920 x 1080 | 60 | 27 | Variable | 5 High | 4:2:2 | 10-bit | Yes |
| Cineform 10-bit HD Medium | 1920 x 1080 | 75 | 34 | Variable | 4 Some | 4:2:2 | 10-bit | Yes |
| Cineform 10-bit UHD Film Scan | 3840 x 2160 | 310 | 140 | Variable | 3 Minor | 4:2:2 | 10-bit | Yes |
| Cineform 10-bit UHD Film Scan 2 | 3840 x 2160 | 580 | 261 | Variable | 2 Minimal | 4:2:2 | 10-bit | Yes |
| Cineform 10-bit UHD High | 3840 x 2160 | 260 | 117 | Variable | 4 Some | 4:2:2 | 10-bit | Yes |
| Cineform 10-bit UHD Low | 3840 x 2160 | 190 | 86 | Variable | 5 High | 4:2:2 | 10-bit | Yes |
| Cineform 10-bit UHD Medium | 3840 x 2160 | 230 | 104 | Variable | 4 Some | 4:2:2 | 10-bit | Yes |
| Cineform 12-bit HD Film Scan | 1920 x 1080 | 230 | 104 | Variable | 2 Minimal | 4:4:4 | 12-bit | Yes |
| Cineform 12-bit HD Film Scan 2 | 1920 x 1080 | 365 | 164 | Variable | 3 Minor | 4:4:4 | 12-bit | Yes |
| Cineform 12-bit HD High | 1920 x 1080 | 195 | 88 | Variable | 4 Some | 4:4:4 | 12-bit | Yes |
| Cineform 12-bit HD Low | 1920 x 1080 | 130 | 59 | Variable | 5 High | 4:4:4 | 12-bit | Yes |
| Cineform 12-bit HD Medium | 1920 x 1080 | 160 | 72 | Variable | 4 Some | 4:4:4 | 12-bit | Yes |
| Cineform 12-bit UHD Film Scan | 3840 x 2160 | 750 | 338 | Variable | 3 Minor | 4:4:4 | 12-bit | Yes |
| Cineform 12-bit UHD Film Scan 2 | 3840 x 2160 | 1,210 | 545 | Variable | 2 Minimal | 4:4:4 | 12-bit | Yes |
| Cineform 12-bit UHD High | 3840 x 2160 | 630 | 284 | Variable | 4 Some | 4:4:4 | 12-bit | Yes |
| Cineform 12-bit UHD Low | 3840 x 2160 | 445 | 200 | Variable | 5 High | 4:4:4 | 12-bit | Yes |
| Cineform 12-bit UHD Medium | 3840 x 2160 | 515 | 232 | Variable | 4 Some | 4:4:4 | 12-bit | Yes |
| DNxHD 444 (a.k.a DNxHD 350x) | 1920 x 1080 | 350 | 158 | Constant | 2 Minimal | 4:4:4 | 10-bit | Yes |
| DNxHD 80 | 1920 x 1080 | 80 | 36 | Constant | 5 High | 4:2:2 | 8-bit | Yes |
| DNxHD HQ (a.k.a DNxHD 175) | 1920 x 1080 | 175 | 79 | Constant | 3 Minor | 4:2:2 | 8-bit | Yes |
| DNxHD HQX (a.k.a DNxHD 175x) | 1920 x 1080 | 175 | 79 | Constant | 3 Minor | 4:2:2 | 10-bit | Yes |
| DNxHD LB (a.k.a DNxHD 36) | 1920 x 1080 | 36 | 16 | Constant | 5 High | 4:2:2 | 8-bit | Yes |
| DNxHD SQ (a.k.a DNxHD 115) | 1920 x 1080 | 115 | 52 | Constant | 4 Some | 4:2:2 | 8-bit | Yes |
| DNxHR 444 | 3840 x 2160 | 1,399 | 630 | Constant | 2 Minimal | 4:4:4 | 12-bit | Yes |
| DNxHR HQ | 3840 x 2160 | 699 | 315 | Constant | 3 Minor | 4:2:2 | 8-bit | Yes |
| DNxHR HQX | 3840 x 2160 | 699 | 315 | Constant | 3 Minor | 4:2:2 | 12-bit | Yes |
| DNxHR LB | 3840 x 2160 | 144 | 65 | Constant | 5 High | 4:2:2 | 8-bit | Yes |
| DNxHR SQ | 3840 x 2160 | 456 | 205 | Constant | 4 Some | 4:2:2 | 8-bit | Yes |
| DPX HD (uncompresssed) | 1920 x 1080 | 1,590 | 716 | Constant | 1 None | 4:4:4 | 10-bit | Yes |
| DPX UHD (uncompressed) | 3840 x 2160 | 6,370 | 2,867 | Constant | 1 None | 4:4:4 | 10-bit | Yes |
| H.264 HD (YouTube settings) | 1920 x 1080 | 8 | 4 | Variable | 5 High | 4:2:0 | 8-bit | Yes |
| H.264 UHD (YouTube settings) | 3840 x 2160 | 40 | 18 | Variable | 5 High | 4:2:0 | 8-bit | Yes |
| ProRes 422 (HD) | 1920 x 1080 | 117 | 53 | Variable | 4 Some | 4:2:2 | 10-bit | No* |
| ProRes 422 (UHD) | 3840 x 2160 | 471 | 212 | Variable | 4 Some | 4:2:2 | 10-bit | No* |
| ProRes 422 HQ (HD) | 1920 x 1080 | 176 | 79 | Variable | 3 Minor | 4:2:2 | 10-bit | No* |
| ProRes 422 HQ (UHD) | 3840 x 2160 | 707 | 318 | Variable | 3 Minor | 4:2:2 | 10-bit | No* |
| ProRes 422 LT (HD) | 1920 x 1080 | 82 | 37 | Variable | 5 High | 4:2:2 | 10-bit | No* |
| ProRes 422 LT (UHD) | 3840 x 2160 | 328 | 148 | Variable | 4 Some | 4:2:2 | 10-bit | No* |
| ProRes 422 Proxy (HD) | 1920 x 1080 | 36 | 16 | Variable | 5 High | 4:2:2 | 10-bit | No* |
| ProRes 422 Proxy (UHD) | 3840 x 2160 | 145 | 65 | Variable | 5 High | 4:2:2 | 10-bit | No* |
| ProRes 4444 (HD) (no alpha) | 1920 x 1080 | 264 | 119 | Variable | 2 Minimal | 4:4:4 | 12-bit | No* |
| ProRes 4444 (UHD) (w/o alpha) | 3840 x 2160 | 1,061 | 477 | Variable | 2 Minimal | 4:4:4 | 12-bit | No* |
| ProRes 4444 XQ (HD) (no alpha) | 1920 x 1080 | 396 | 178 | Variable | 2 Minimal | 4:4:4 | 12-bit | No* |
| ProRes 4444 XQ (UHD ) (w/o alpha) | 3840 x 2160 | 1,591 | 716 | Variable | 2 Minimal | 4:4:4 | 12-bit | No* |
| Uncompressed HD 10-bit 4:4:4 | 1920 x 1080 | 1,490 | 671 | Constant | 1 None | 4:4:4 | 10-bit | Yes |
| Uncompressed HD 8-bit 4:4:4 | 1920 x 1080 | 1,192 | 536 | Constant | 1 None | 4:4:4 | 8-bit | Yes |
| Uncompressed UHD 10-bit 4:4:4 | 3840 x 2160 | 5,970 | 2,687 | Constant | 1 None | 4:4:4 | 10-bit | Yes |
| Uncompressed UHD 8-bit 4:4:4 | 3840 x 2160 | 4,780 | 2,151 | Constant | 1 None | 4:4:4 | 8-bit | Yes |
*Table made by Frame.io
Uncompressed Data Rates:
*calculated by:
3 x colour depth x vertical resolution x horizontal resolution x framerate
eg. 3 x 8-bit x 1080 x 1920 x 25 = 1244160000 bits/s = 148Mb/s
-
24fps HD:
25fps HD:
30fps HD:
24fps UHD:
25fps UHD:
30fps UHD:
24fps DCI 4K:
25fps DCI 4K:
30fps DCI 4K:
-
24fps HD:
25fps HD:
30fps HD:
24fps UHD:
25fps UHD:
30fps UHD:
24fps DCI 4K:
25fps DCI 4K:
30fps DCI 4K:
-
24fps HD:
25fps HD:
30fps HD:
24fps UHD:
25fps UHD:
30fps UHD:
24fps DCI 4K:
25fps DCI 4K:
30fps DCI 4K:
-
24fps HD:
25fps HD:
30fps HD:
24fps UHD:
25fps UHD:
30fps UHD:
24fps DCI 4K:
25fps DCI 4K:
30fps DCI 4K:
-
24fps HD:
25fps HD:
30fps HD:
24fps UHD:
25fps UHD:
30fps UHD:
24fps DCI 4K:
25fps DCI 4K:
30fps DCI 4K:
-
Rather don’t
24fps HD:
25fps HD:
30fps HD:
24fps UHD:
25fps UHD:
30fps UHD:
24fps DCI 4K:
25fps DCI 4K:
30fps DCI 4K:
Hardware Specifications:
Storage Media | Interconnects | Interfaces | Software
Interconnects:
-
Description text goes here
-
Description text goes here
-
Description text goes here
-
Item description
Interfaces:
-
Description text goes here
-
Description text goes here
-
Description text goes here
Storage Media:
Camera Cards:
Codex
SSD
CFast
SD
Storage Media:
SSD
HDD
Archive Media:
LTO
Tools
ARRI Data Rate Calculator
https://www.arri.com/en/learn-help/learn-help-camera-system/tools/formats-and-data-rate-calculator
Audio Bit-Rate and File Size Calculator:
https://www.theaudioarchive.com/TAA_Resources_File_Size.htm
Data Management
ISO 8601 filenaming standard: YYYY-MM-DD.
Design
Windows:
256x256 max/recommended resolution